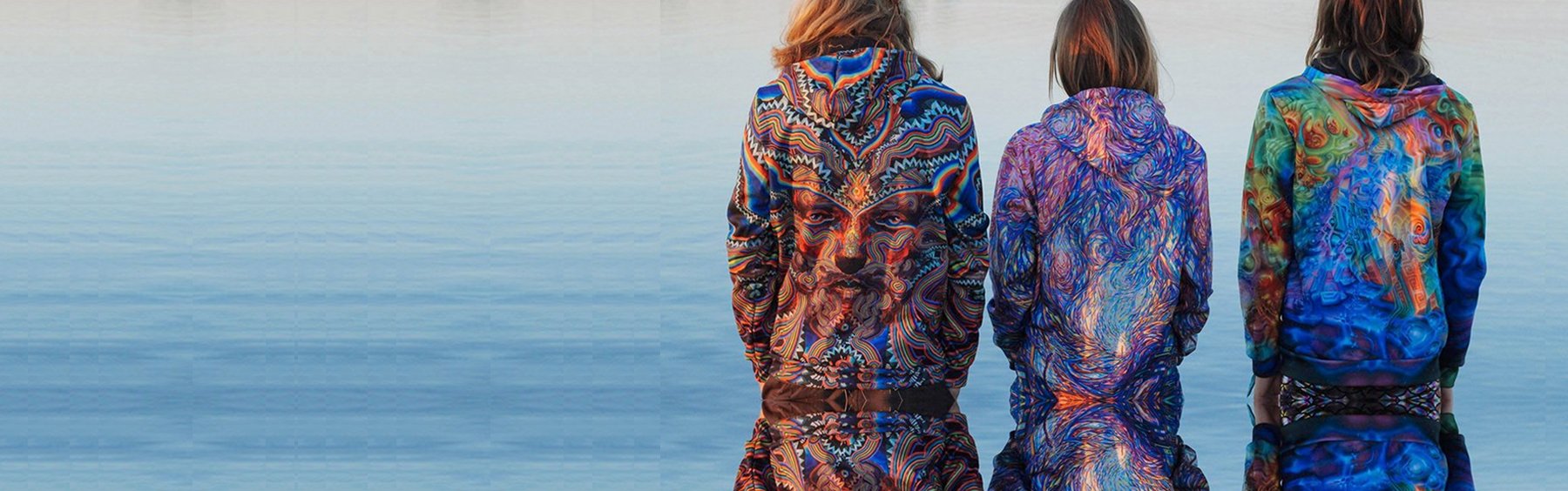
The fashion world is evolving constantly. Dyeing methods play a big role in shaping the look and feel of apparels. There are various methods available and garment dyeing has become very popular, especially in streetwear and casual wear. As compared to traditional dyeing methods, where fabric is colored first, before being cut and stitched, garment dyeing is focused on coloring the fully finished garment. This single alteration in process results in major differences – in softness, texture and overall appeal. Find out about the top differences between garment dyeing and regular dyeing, and what sets them apart from each other.
Garment dyeing is a process favored particularly for casualwear, like sweatshirts, jackets, hoodies and T-shirts, where comfort and individuality are more essential than formality. It produces a textured and slightly faded look, which is impossible to achieve through regular dyeing practices.
In this process, clothes are dyed after they have already been cut, stitched and finished. Rather than treating raw fabric, the entire clothing item – complete with buttons, zippers and stitching – is immersed in dye.
Due to this approach, it is possible to provide garments with a special look. It often creates subtle tonal variations, vintage-inspired hues and a slightly distressed finish. While regular dyeing aims for uniformity, garment dyeing allows imperfections. It leads to garments with a used, lived-in feel that appeals to stylish consumers.

The whole process includes a number of steps that are managed carefully. It starts with preparing the finished garment, often composed of natural fibers like wool, linen or cotton. Once the garment is sewn together, including accessories and trims, it is soaked in a dye bath. The choice of dye depends on the composition of the fiber. For natural fabrics, fiber-reactive dyes are used commonly, as these bond with the fibers chemically – ensuring stronger retention of colors.
Then, the garments are tumbled and rotated within dyeing machines or vats. It allows the dye to penetrate folds, seams and textured areas in a uniform manner. This leads to the signature shade variations and tonal depth that garment dyeing is popular for.
After the dyeing process is complete, the garments may go through chemical treatments or washing, to lend them their unique finish or distressed effects.
Ultimately, they are dried and softened, to give them the desired handcrafted feel. The garments look lived-in yet fashionable, with colors and textures exuding a unique, authentic look.
The timing of the color application is the main difference between the two types of dyeing. In garment dyeing, the dyeing occurs after the apparel is prepared. In contrast, the fabric is dyed before it is cut and stitched, in case of regular dyeing.
In piece dyeing, it is possible to get a uniform, consistent shade across an entire fabric batch. Due to this reason, it is perfect for large-scale production, where it is critical to ensure consistency – such as for corporate apparels, uniforms or formalwear. But it does not have the variation and uniqueness that can be expected from the garment dyeing process.
On the other hand, the garment dyeing process is less predictable inherently. The trims, layers and seams of a garment may absorb dye in a different way, leading to a washed or marled effect. However, for fashionable consumers who want to make a statement of individuality through their clothing, such imperfections are major advantages. For brands targeting lifestyle apparel, casual wear or streetwear, the garment dyeing process adds a level of character that cannot be replicated with piece dyeing.

One of the topmost advantages of garment dyeing is possibly the texture that it is able to create. As the dyeing process starts after the garment is sewn, the fibers go through additional mechanical stress during washing and finishing. It makes the fabric softer and leads to a broken-in feel that would generally take many years to achieve normally. Customers often describe clothing items made with the garment dyeing process as more comfortable, right from the first time that they wear them.
Other than the softness, it is possible to get a more dimensional and richer color palette. There is an uneven absorption of dye across folds and seams, which improves the depth of the color of the garments. This leads to shades that shift subtly in different lighting conditions. While regular dyeing leads to flat and uniform colors, garment dyeing adds vibrancy and personality to casualwear. Due to this reason, it is especially popular for lifestyle clothing, denim and outerwear items that stand out with an authentic, rugged aesthetic.
It is essential to note that not every fabric is well suited for this process. Natural fibers like linen, wool and cotton are best, as these can readily absorb dye and lead to durable, vibrant results. Casual jackets, sweatshirts and cotton t-shirts are among the most common products that are garment-dyed, because the material displays depth of color wonderfully, while staying breathable and soft. Denim happens to be another popular choice, given that garment dyeing improves its lived-in feel and leads to the vintage finish that customers demand so much.
Nylon, polyester and other synthetic fabrics are not so much responsive to this type of dyeing process. While these can be treated with special dyes, the results are not much vibrant. The same level of softness cannot be expected from the fabric. Moreover, there are challenges like uneven absorption or shrinkage in case of synthetic dyes, which can complicate the process. Manufacturers need to assess their selection of fabric carefully, to ensure the intended results from the garment dyeing process.

Today, the garment dyeing process has become a staple dyeing method for both streetwear and casualwear clothing items. Whether it comes to sun-faded jackets or washed hoodies, the process denotes a cultural shift toward sustainability, individuality and authenticity. The lived-in look has become synonymous with relaxed style. It makes the garment dyeing process very important for designers who want to be outstanding in a competitive market. Whether you are a retailer or a private label seller, you would love to keep clothing items in your product line that are the results of garment dying process, to cater to stylish customers who are high on individuality.